2.3. Natural Systems are Vulnerable to Climate Change, and Some will be Irreversibly
Damaged
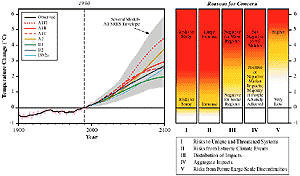
Figure SPM-2: Reasons for concern about projected climate change
impacts. The risks of adverse impacts from climate change increase with
the magnitude of climate change. The left part of the figure displays the
observed temperature increase relative to 1990 and the range of projected
temperature increase after 1990 as estimated by Working Group I of the IPCC
for scenarios from the Special Report on Emissions Scenarios. The right
panel displays conceptualizations of five reasons for concern regarding
climate change risks evolving through 2100. White indicates neutral or small
negative or positive impacts or risks, yellow indicates negative impacts
for some systems or low risks, and red means negative impacts or risks that
are more widespread and/or greater in magnitude. The assessment of impacts
or risks takes into account only the magnitude of change and not the rate
of change. Global mean annual temperature change is used in the figure as
a proxy for the magnitude of climate change, but projected impacts will
be a function of, among other factors, the magnitude and rate of global
and regional changes in mean climate, climate variability and extreme climate
phenomena, social and economic conditions, and adaptation. |
Natural systems can be especially vulnerable to climate
change because of limited adaptive capacity (see Box SPM-1),
and some of these systems may undergo significant and irreversible damage. Natural
systems at risk include glaciers, coral reefs and atolls, mangroves, boreal
and tropical forests, polar and alpine ecosystems, prairie wetlands, and remnant
native grasslands. While some species may increase in abundance or range, climate
change will increase existing risks of extinction of some more vulnerable species
and loss of biodiversity. It is well-established6 that the geographical extent
of the damage or loss, and the number of systems affected, will increase with
the magnitude and rate of climate change (see Figure SPM-2).
[4.3 and 7.2.1]
2.4. Many Human Systems are Sensitive to Climate Change,
and Some are Vulnerable
Human systems that are sensitive to climate change include mainly water resources;
agriculture (especially food security) and forestry; coastal zones and marine
systems (fisheries); human settlements, energy, and industry; insurance and
other financial services; and human health. The vulnerability of these systems
varies with geographic location, time, and social, economic, and environmental
conditions. [4.1, 4.2, 4.3,
4.4, 4.5, 4.6,
and 4.7]
Projected adverse impacts based on models and other studies include:
- A general reduction in potential crop yields in most tropical and sub-tropical
regions for most projected increases in temperature [4.2]
- A general reduction, with some variation, in potential crop yields in most
regions in mid-latitudes for increases in annual-average temperature of more
than a few °C [4.2]
- Decreased water availability for populations in many water-scarce regions,
particularly in the sub-tropics [4.1]
- An increase in the number of people exposed to vector-borne (e.g., malaria)
and water-borne diseases (e.g., cholera), and an increase in heat stress mortality
[4.7]
- A widespread increase in the risk of flooding for many human settlements
(tens of millions of inhabitants in settlements studied) from both increased
heavy precipitation events and sea-level rise [4.5]
- Increased energy demand for space cooling due to higher summer temperatures.
[4.5]
Projected beneficial impacts based on models and other studies include:
- Increased potential crop yields in some regions at mid-latitudes for increases
in temperature of less than a few °C [4.2]
- A potential increase in global timber supply from appropriately managed
forests [4.3]
- Increased water availability for populations in some water-scarce regions—for
example, in parts of southeast Asia [4.1]
- Reduced winter mortality in mid- and high-latitudes
- Reduced energy demand for space heating due to higher winter temperatures.
[4.5]
|
Box SPM-1. Climate Change
Sensitivity, Adaptive Capacity, and Vulnerability
Sensitivity is the degree to which a system is affected, either adversely
or beneficially, by climate-related stimuli. Climate-related stimuli encompass
all the elements of climate change, including mean climate characteristics,
climate variability, and the frequency and magnitude of extremes. The
effect may be direct (e.g., a change in crop yield in response to a change
in the mean, range, or variability of temperature) or indirect (e.g.,
damages caused by an increase in the frequency of coastal flooding due
to sea-level rise).
Adaptive capacity is the ability of a system to adjust to climate change
(including climate variability and extremes) to moderate potential damages,
to take advantage of opportunities, or to cope with the consequences.
Vulnerability is the degree to which a system is susceptible to, or unable
to cope with, adverse effects of climate change, including climate variability
and extremes. Vulnerability is a function of the character, magnitude,
and rate of climate change and variation to which a system is exposed,
its sensitivity, and its adaptive capacity.
|
2.5. Projected Changes in Climate Extremes could have Major
Consequences
The vulnerability of human societies and natural systems to climate extremes
is demonstrated by the damage, hardship, and death caused by events such as
droughts, floods, heat waves, avalanches, and windstorms. While there are uncertainties
attached to estimates of such changes, some extreme events are projected to
increase in frequency and/or severity during the 21st century due to changes
in the mean and/or variability of climate, so it can be expected that the severity
of their impacts will also increase in concert with global warming (see Figure
SPM-2). Conversely, the frequency and magnitude of extreme low temperature
events, such as cold spells, is projected to decrease in the future, with both
positive and negative impacts. The impacts of future changes in climate extremes
are expected to fall disproportionately on the poor. Some representative examples
of impacts of these projected changes in climate variability and climate extremes
are presented in Table SPM-1. [3.5,
4.6, 6, and 7.2.4]
